Spring Boot 3 updates over Spring Boot2
Introduction
As we know SpringBoot 3 internally uses Spring 6. In Spring 6, the Spring Committee brought in something called RFC7807, also known as "Problem Details for HTTP APIs.".
This is useful in cases where HTTP status codes are not enough to describe the problem with an HTTP API.
It's like a rulebook that says errors or issues in HTTP APIs should be explained in a specific and more detailed way. ProblemDetail improves error troubleshooting by responding with an error message in a special style using methods like errorType(), errorTitle(), errorDetail(), and many more in JSON format.
why it was required to introduce a new class?
When you're working on a RESTful API, it's super important to handle errors gracefully and give clients clear information when things go wrong.
Spring Boot 3 has this cool thing called the ProblemDetail specification, which helps you create standardized and organized error responses. In this blog post, we're going to deep dive into how to use this feature in our Spring Boot applications.
The advantage is that API designers don't have to devise their own methods for describing problem details.
Creating custom error messages for a customer REST application in a specific JSON format is important. The HTTP status often does not provide enough information for the client. Therefore, more detailed information about the issue must be sent back to the client side.
To accomplish this, previously we had to create our own Error class. It's a common requirement for REST applications to provide detailed error responses. This is where the Problem Details Class for HTTP API specification (code RFC 7807) becomes useful.
Its purpose is to define common error formats in HTTP responses, eliminating the need for each application to define its own.
We'll explore how it can make handling exceptions easier and allow you to create custom error responses that make sense for your application.
Problem Statement: We will write a rest API method to register the vote of a person. If the person is above 18 years old, that person can vote and we will register his/her vote. If his/her age is less than or equal to 18 we will generate an exception and we will try to handle that generated exception with proper error details sent back to the client side with the help of the ProblemDetail Class object.
Note: We will be focusing on generating a custom exception by passing the age value smaller than or equal to 18 and then handling the exception object and providing error details to the client with the help of the ProblemDetail Class.So, that we can understand how ProblemDetail Class works.
Step1:
Creating a rest controller class and defining a controller method named vote to register the vote. Certainly! Here's a revised and clear explanation:
In the upcoming sections of this article, we will be creating a custom exception class named AgeNotValidException. This class will be utilized in a REST controller method called vote. If the age of the voter is less than or equal to 18, the vote method will throw an instance of the AgeNotValidException. This approach allows us to handle cases where the voter's age is not within the acceptable range gracefully.

Step2
Creating a service class and defining the method registerVote to process the logic of registering votes and passing the age of the voter in the method parameter.

Step3
Creating our custom Exception Class i.e. AgeNotValidException. When the age of the voter is below 19, we will throw an object of this custom-generated exception class which will be further handled by another rest exception controller method.

Step4
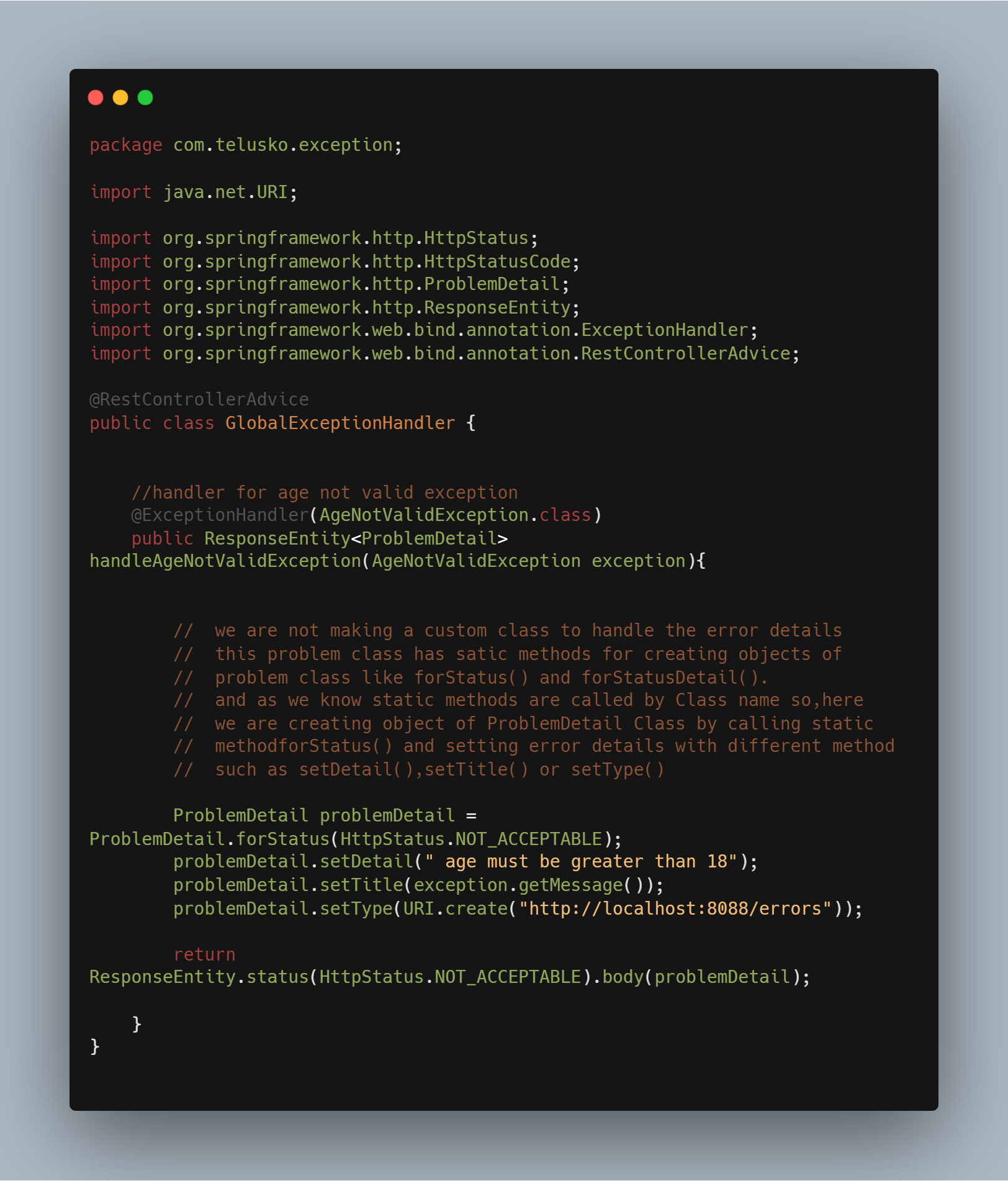
Creating a rest Controller exception class and naming it GlobalExceptionHandler for intercepting custom exceptions.
When a user enters an age less than or equal to 18, our rest controller method i.e. vote is going to throw an object of this AgeNotValidException class.
We have created another rest controller i.e. GlobalExceptionHandler just to handle custom exception objects thrown by the method i.e. vote present in our primary rest controller class i.e. ControllerClassForProblemClassExplaination.
we have defined a controller method i.e. handleAgeNotValidException for handling AgeNotValidException exception objects thrown by the vote method.
In this handleAgeNotValidException method, we will create an object of the ProblemDetail class and we will inject error details into that object.
ProblemDetail class object has certain methods i.e. setDetail(), setType(), setTitle(), and many more inbuilt methods which can be used to pass more information about the error at the client side.
setDetail() -> This method is used to set details of the error, to have a better understanding of the error at the client side whenever it occurs.
The same goes for setTitle() and many more methods.
Explanation of the above code:
we are not making a custom class to handle the error details.
This ProblemDetail class has static methods for creating objects like forStatus() and forStatusDetail() which we will use for handling and setting error details.
In simpler terms, static methods are invoked using the class name. In this context, we're making an object of the ProblemDetail Class by using the static method forStatus(). Then, we're configuring error details by calling various built-in methods on the ProblemDetail Class object, which we've named "problemDetail." These methods include setDetail(), setTitle(), or setType().
Step5
we have sent a post request with the age value=11 in the query string with the help of @Requestparam annotation. As the age of the voter is less than 19, it returns the detailed error message instead of generating some random error messages that can't be understood by us.

Below is the detailed error that is being sent to the client in JSON format using the object of ProblemDetail Class. It has information like error type, title, detail, status code, and path for which the error is generated. This error information can be further used for error-solving much more easily. It can save a lot of time as we don't have to debug much, like from where this error is getting generated in our code.

For more reference
please have a look at the official documentation :
Let's Connect:
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/gaurav4044/
Github: https://github.com/Gaurav560
