Table of contents
Prerequisites:
Good practical knowledge of Core Java(specially oops concepts like Inheritance, Polymorphism, Interface, Classes, Objects, etc. Exception Handling, and multi-threading). Basic practical Knowledge of SQL and have worked on any Database WorkBench. Creating Databases and Tables, Insertion, deletion, updation, and storage of data in tables. selection of particular data from a table in a database.
What is Jdbc?
JDBC is a Java API that Sun Micro-Systems(Creator of Java) gave to connect the java program to any databases. with the help of Jdbc, we can perform different operations in our database such as searching for any data stored in the database, insertion of data, deletion of data, and updation of data, and many more things through our java program.
Now u will ask, what is an API?
An API is nothing but a collection of predefined interfaces and classes in java. There are two types of API, one is user-defined API which we can write manually according to our needs and another type is java built-in API which is given by Sun Microsystems for use. jdbc is also a built-in API.
Setting up the environment:
1. How the connection takes place between java and any database()?
There are some predefined interfaces and classes written in jdbc api , if any java program needs to connect to any database, then the database company has to implement those interfaces and classes written in JDBC API and write their own program in sync with JDBC. Those programs are called driver files(also called connector files). These driver files are then compressed and stored in a jar file.
2. Setting up the Class Path Variable
We have to tell Java, where our jar or connector file is on the computer. For that, you can go to settings-> System Properties->Advanced->Environmnetal Variables->User Variables->ClassPath. In the classpath, edit the classpath and add the location of the jar file installed on your computer. NOTE: If classPath is not available in the user variables then, add the classpath in user variables and then add the location of the jar file in the classpath.
JDBC Architecture
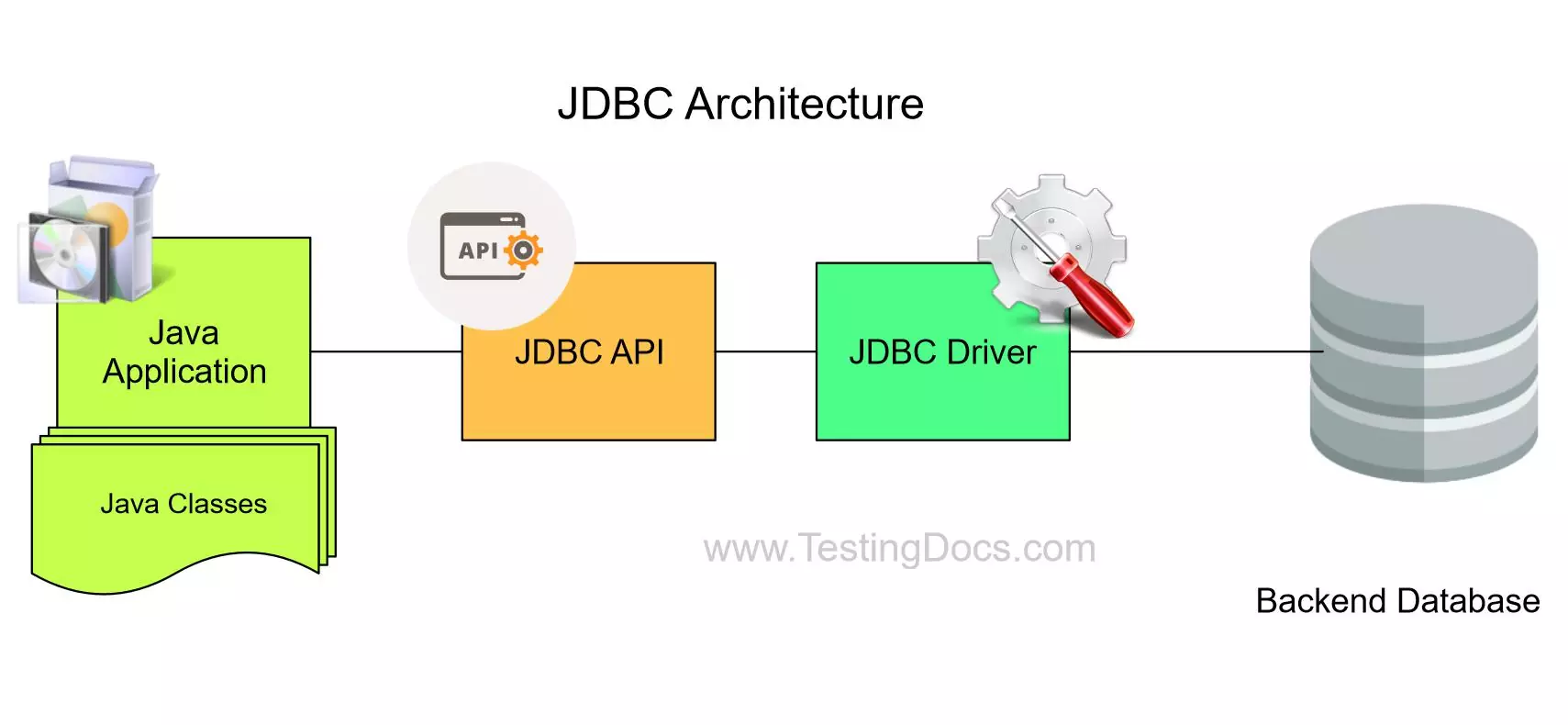 image source: TestingDocs.com
image source: TestingDocs.com
key points: In SQL with a java perspective, there are only two types of queries
- SELECT queries(if we have to search anything from the database.)
- NON-SELECT queries(which includes insertion,deletion,updation)
And within these commands, there are two types also.
- those queries in which we know what we have to search, insert, delete, or update before the runtime of queries.
- those queries for which we have to dynamically insert, search, update, or delete data at runtime.
Now, in this article, we are taking a select query example (data in the query will be already inserted before runtime) to understand common steps to execute a normal query. Once you will understand the query executions through the java program, other modifications will be a cakewalk for you. note: i will be using the MySQL database and its connector(jar file) to connect our java program to the MySQL database for the below examples.
Important: Six Steps one must consider in mind while executing a query through jdbc API :
- loading of driver class of MySQL database
- creating a connection object to establish a connection between the program and the database.
- Creating a statement object to execute the query.
- creating a resultset object to process the results we get back from the query.
- handle exceptions if arises.
- close the resources so it does not get wasted. (1st,2nd,5th, and 6th steps are common in almost every query. modifications are done in 3rd and 4th steps as per requirement.)
java program for select query from a database named 'gauravdb' which I have created in MySQL workbench.
import java.sql.*;
class TestApp
{
public static void main (String []args)
{
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try
{
System.out.println("loading and registering the driver ");
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("driver loaded successfully.....");
System.out.println("hooray u are too good to be true .");
System.out.println("2ndStep establishing theconnection :");
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/gauravdb";
String username="root";
String password="Lumia@540";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
System.out.println("Connection established successfully");
System.out.println("the implement class name is :"+connection.getClass().getName());
System.out.println("3rd step creating statement and resultset object and sending the query");
String sqlSelectQuery="select name,pnumber,age from studentinfo";
statement=connection.createStatement();
System.out.println("the implementation class name for statement interface is "+statement.getClass().getName());
resultSet=statement.executeQuery(sqlSelectQuery);
System.out.println("the implementation class name for resultSet interface is "+resultSet.getClass().getName());
System.out.println("Step 4:process the resultSet");
System.out.println("name\tpnumber\t\tage");
while(resultSet.next())
{
String name=resultSet.getString(1);
String pnumber=resultSet.getString(2);
Integer age=resultSet.getInt(3);
System.out.println(name+"\t"+pnumber+"\t"+age);
}
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException ce)
{
ce.printStackTrace();
}
catch(SQLException se)
{
se.printStackTrace();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
if(connection!=null)
{
try
{
connection.close();
}
catch(SQLException se)
{
se.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println("closing the database........");
}
}
output:
loading the driver class
establishing a connection with mysql databse
creating a connection object
the implement className for connection interface is is :com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl
creating a statement object
the implement className for statement interface is is :com.mysql.cj.jdbc.StatementImpl
creating a resultSet object
the implement className for resultSet interface is is :com.mysql.cj.jdbc.result.ResultSetImpl
processing the resultSet
name pnumber age
sameer 9801553556 18
ankit 7055460768 23
gaurav 980154446 24
ankit 7055460768 23
shweta 9234676768 25
amar 8340532368 24
divya 73660492211 19
closing the resources
note:
- Connection, Statement, and ResultSet classes are all present in the java.sql package that's why I have imported java.sql.* .
- And the username and password will be, which u have given while creating MySQL workbench.
- The URL will be same for all as data is stored locally in databse except the database name at last(in my case it is gauravdb)
*Other Queries will be explained in the upcoming articles as too many queries in a single blog will make the blog lengthy and complex. Subscribe to my news letter to never miss an article.
